

2023 , Vol. 20 >Issue 09: 895 - 903
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2023.09.002
基于高帧频超声造影的影像组学特征鉴别诊断甲状腺结节良恶性的价值
Copy editor: 吴春凤
收稿日期: 2023-06-07
网络出版日期: 2023-12-11
版权
Value of radiomics features based on high-frame-rate contrast-enhanced ultrasound in differential diagnosis of benign and malignant thyroid nodules
Received date: 2023-06-07
Online published: 2023-12-11
Copyright
评估从甲状腺灰阶超声图像、常规超声造影(CEUS)及高帧频超声造影(H-CEUS)图像中提取的影像组学特征对于甲状腺结节良恶性诊断的价值及其诊断效能。
回顾性收集并最终纳入2021年1月至2022年4月中国医科大学附属盛京医院的186例患者的186个结节的灰阶超声图像、常规CEUS及H-CEUS视频数据,分别选择灰阶超声图像中结节最大长轴的横向切面、纵向切面以及常规CEUS和H-CEUS视频中造影剂到达时间、达峰时间、平均消退时间对应的3个关键帧图像这8张图像进行分析并提取相应的影像组学特征,采用逻辑回归和随机森林建立3种影像组学模型(灰阶超声、灰阶超声+常规CEUS和灰阶超声+H-CEUS模型),最后,评估这些影像组学特征的诊断效能,比较3种模型在测试集(38个结节)中的曲线下面积(AUC)、敏感度、特异度、阳性预测值(PPV)、阴性预测值(NPV)、准确性、F1评分。
共提取186例患者186个结节的9000个影像组学特征,灰阶超声模型在测试集中的AUC、准确性、敏感度、特异度、PPV、NPV和F1评分分别为0.81、81.6%、68.8%、90.9%、84.6%、80.0%和0.76。灰阶超声+常规CEUS模型在测试集中的AUC、准确性、敏感度、特异度、PPV、NPV和F1评分分别为0.87、84.2%、68.8%、95.5%、91.7%、80.8%和0.79。灰阶超声+H-CEUS模型在测试集中的AUC、准确性、敏感度、特异度、PPV、NPV和F1评分分别为0.91、86.8%、87.5%、86.4%、82.4%、90.5%和0.85。
基于灰阶超声图像、常规CEUS和H-CEUS关键帧图像的影像组学特征对于鉴别良恶性甲状腺结节具有一定价值,灰阶超声+H-CEUS图像的影像组学模型的诊断效能优于灰阶超声模型和灰阶超声+常规CEUS影像组学模型。
张茜 , 陈佳慧 , 高雪萌 , 赵傲雪 , 黄瑛 . 基于高帧频超声造影的影像组学特征鉴别诊断甲状腺结节良恶性的价值[J]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2023 , 20(09) : 895 -903 . DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2023.09.002
To evaluate the clinical application and diagnostic efficiency of the radiomics features extracted from thyroid B-mode ultrasound (B-US) images, contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) images, and high-frame-rate contrast-enhanced ultrasound (H-CEUS) images in classifying and predicting benign and malignant thyroid nodules.
We retrospectively collected and ultimately included B-US images, CEUS videos, and H-CEUS videos of 186 nodules from 186 patients. Next, we selected the following eight images to manually select the regions of interest: nodule in transverse section, nodule in longitudinal section, and the "rise time" frame, "time to peak" frame, and "mean transit time" frame of both CEUS and H-CEUS videos, and then extracted the corresponding radiomics features from these images. We established three radiomics models (B-US radiomics model, B-US+CEUS radiomics model, and B-US+H-CEUS radiomics model) based on these radiomics features by Logistic regression and random forest, and assessed the diagnostic performance of these radiomics features. Finally, the area under curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV), accuracy (ACC), and F1-score in the test set (n=38) were calculated and compared.
A total of 9000 significant radiomics features of 186 nodules from 186 patients were extracted. The AUC in the differential diagnosis of the nature of thyroid nodules was 0.81 for the B-US radiomics model, 0.87 for the B-US+CEUS radiomics model, and 0.91 for the B-US+H-CEUS radiomics model. The accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and F1 scores of the B-US radiomics model in the test set were 81.6%, 68.8%, 90.9%, 84.6%, 80.0%, and 0.76, respectively; the corresponding values were 84.2%, 68.8%, 95.5%, 91.7%, 80.8%, and 0.79 for the B-US+CEUS radiomics model, and 86.8%, 87.5%, 86.4%, 82.4%, 90.5%, and 0.85 for the B-US+H-CEUS radiomics model.
Radiomics features based on B-US images, CEUS, and H-CEUS key frame images have appreciated clinical value in differentiating benign and malignant thyroid nodules. The diagnostic efficacy of the B-US+H-CEUS radiomics model is better than that of other radiomics models.
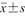 表示,采用t检验比较良恶性结节组间差异;结节最大径为不符合正态分布的计量资料,采用M(QR)表示,采用Mann-Whitney U检验比较2组间差异;余资料均为计数资料,采用例数(%)表示,采用χ2检验和Fisher精确概率检验比较2组间差异。绘制受试者操作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线,评价3种超声诊断模型的诊断效能,通过曲线下面积(area under curve,AUC)、准确性、敏感度、特异度、阳性预测值(positive predictive value,PPV)、阴性预测值(negative predictive value,NPV)和F1评分评估模型在结节分类中的效能,并计算敏感度、特异度、PPV、NPV的95%可信区间。以P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
表示,采用t检验比较良恶性结节组间差异;结节最大径为不符合正态分布的计量资料,采用M(QR)表示,采用Mann-Whitney U检验比较2组间差异;余资料均为计数资料,采用例数(%)表示,采用χ2检验和Fisher精确概率检验比较2组间差异。绘制受试者操作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线,评价3种超声诊断模型的诊断效能,通过曲线下面积(area under curve,AUC)、准确性、敏感度、特异度、阳性预测值(positive predictive value,PPV)、阴性预测值(negative predictive value,NPV)和F1评分评估模型在结节分类中的效能,并计算敏感度、特异度、PPV、NPV的95%可信区间。以P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。表1 不同超声组学模型对测试集甲状腺结节的诊断结果 |
| 诊断模型 | 病理结果 | |
|---|---|---|
| 良性 | 恶性 | |
| 灰阶超声 | ||
| 良性 | 11 | 2 |
| 恶性 | 5 | 20 |
| 灰阶超声+常规CEUS | ||
| 良性 | 11 | 1 |
| 恶性 | 5 | 21 |
| 灰阶超声+H-CEUS | ||
| 良性 | 14 | 3 |
| 恶性 | 2 | 19 |
注:CEUS为超声造影,H-CEUS为高帧频超声造影 |
表2 良恶性甲状腺结节组一般临床资料及影像特征比较 |
| 项目 | 恶性结节组(n=108) | 良性结节组(n=78) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
年龄(岁,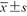 ) ) | 43.06±11.51 | 46.54±12.30 | t=1.973 | 0.050 |
| 性别[例(%)] | χ2=2.905 | 0.088 | ||
| 男 | 21(19.44) | 8(10.26) | ||
| 女 | 87(80.56) | 70(89.74) | ||
| 结节最大径[mm,M(QR)] | 7.0(5.0,10.0) | 12.5(9.0,26.0) | Z=6.076 | <0.001 |
| 结节内部成分[例(%)] | ||||
| 实性 | 108(100) | 69(88.46) | - | <0.001 |
| 非实性 | 0(0) | 9(11.54) | ||
| 纵横比[例(%)] | χ2=22.965 | <0.001 | ||
| ≥1 | 44(40.74) | 7(8.97) | ||
| <1 | 64(59.26) | 71(91.03) | ||
| 内部钙化[例(%)] | χ2=5.454 | 0.020 | ||
| 有微钙化 | 36(33.33) | 14(17.95) | ||
| 无微钙化 | 72(66.67) | 64(82.05) | ||
| 灌注强度[例(%)] | χ2=17.330 | <0.001 | ||
| 高灌注 | 9(8.33) | 25(32.05) | ||
| 等灌注 | 33(30.56) | 20(25.64) | ||
| 低灌注 | 66(61.11) | 33(42.31) | ||
| 灌注模式[例(%)] | χ2=9.033 | 0.003 | ||
| 不均匀 | 48(44.44) | 18(23.08) | ||
| 均匀 | 60(55.56) | 60(76.92) | ||
| 灌注方式[例(%)] | χ2=21.099 | <0.001 | ||
| 向心性 | 38(35.19) | 5(6.41) | ||
| 非向心性 | 70(64.81) | 73(93.59) | ||
| TI-RADS分级[例(%)] | - | <0.001 | ||
| 3级 | 0(0) | 5(6.41) | ||
| 4a级 | 28(25.93) | 50(64.10) | ||
| 4b级 | 41(37.96) | 19(24.36) | ||
| 4c级 | 39(36.11) | 4(5.13) |
注:TI-RADS为甲状腺影像报告与数据系统,-表示采用Fisher确切概率法,无相应统计值 |
图2 恶性结节常规超声造影图像及高帧频超声造影(H-CEUS)图像。该结节细针穿刺病理结果为“Bethesda Ⅵ”,甲状腺乳头状癌;图a为常规超声造影到达时刻图像;图b为常规超声造影达峰时刻图像;图c为常规超声造影平均消退时刻图像;图d为H-CEUS到达时刻图像;图e为H-CEUS达峰时刻图像;图f为H-CEUS平均消退时刻图像。本图中常规超声造影帧频为15帧/s,H-CEUS帧频为87帧/s |
表3 3种诊断模型对测试集中甲状腺结节良恶性的诊断效能 |
| 诊断模型 | 准确性(%) | 敏感度(%) | 特异度(%) | PPV(%) | NPV(%) | F1评分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灰阶超声 | 81.6 | 68.8(44.4~85.8) | 90.9(72.2~97.5) | 84.6(57.8~95.7) | 80.0(60.9~91.1) | 0.76 |
| 灰阶超声+常规CEUS | 84.2 | 68.8(44.4~85.8) | 95.5(78.2~99.2) | 91.7(64.6~98.5) | 80.8(62.1~91.5) | 0.79 |
| 灰阶超声+H-CEUS | 86.8 | 87.5(64.0~96.5) | 86.4(0.66.7~95.3) | 82.4(59.0~93.8) | 90.5(71.1~97.4) | 0.85 |
注:CEUS为超声造影,H-CEUS为高帧频超声造影,PPV为阳性预测值,NPV为阴性预测值;括号内数据为相应指标的95%可信区间 |
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
李楠, 梁舒媛, 费翔, 等. 高帧频超声造影对颈动脉粥样硬化斑块内新生血管的评价价值 [J/OL]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2020, 17(9): 854-859.
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
任玲, 费翔, 张艳, 等. 高帧率超声造影对颈部浅表淋巴结病变良恶性的鉴别诊断 [J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2021, 29(10): 989-992, 997.
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
韩鹏, 费翔, 罗渝昆, 等. 高帧频超声造影在鉴别诊断胆囊腺瘤性息肉与胆固醇性息肉中的临床应用 [J/OL]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2020, 17(9): 815-820.
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |