

2023 , Vol. 20 >Issue 12: 1242 - 1247
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2023.12.004
超声高清微血流成像技术在鉴别乳腺良恶性结节中的应用价值
Copy editor: 汪荣
收稿日期: 2022-11-21
网络出版日期: 2024-03-05
版权
Value of ultrasonic high-definition micro-flow imaging in differentiation of benign and malignant breast masses
Received date: 2022-11-21
Online published: 2024-03-05
Copyright
评估超声高清微血流成像(HD-MFI)技术在鉴别乳腺结节良恶性中的应用价值。
这是一项前瞻性研究。选取2022年3月至2022年6月于中国人民解放军总医院第一医学中心行乳腺常规超声检查提示BI-RADS 3~5类的结节,所有结节均最终获得病理结果。所有结节均分别行彩色多普勒血流成像(CDFI)及HD-MFI扫查,以获得结节的血流情况,并通过HD-MFI获得结节的微血管模式(无血管、线状、树枝状、毛根样及蟹足样)。比较CDFI及HD-MFI对良性结节与恶性结节的血流检出情况及良性结节与恶性结节HD-MFI微血管模式的差异,通过ROC曲线对比分析CDFI与HD-MFI对乳腺结节良恶性的诊断效能。
最终共纳入114例患者的119个乳腺结节,其中71个为良性结节,48个为恶性结节。HD-MFI较CDFI可以更多地检测出乳腺结节的3级血流信号(72.3% vs 20.1%)。在HD-MFI中,良恶性结节均多为2、3级血流信号,但恶性结节的3级血流信号比例显著高于良性结节(85.4% vs 63.4%,P<0.05)。HD-MFI显示良性结节多为无血管、线状或树枝样血管模式,恶性结节多为毛根样或蟹足样模式,微血管模式差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。HD-MFI对乳腺结节良恶性的诊断特异度(91.5% vs 81.7%)、准确度(86.6% vs 82.4%)、阳性预测值(86.4% vs 75.5%)及曲线下面积[0.854(95%CI:0.777~0.912)vs 0.825(95%CI:0.745~0.889)]均高于CDFI。
与CDFI相比,HD-MFI可以更敏感地检出乳腺结节的血流信号,其描绘的血管模式可以为乳腺结节良恶性的鉴别诊断提供更多的血流信息。
罗润兰 , 蒋文莉 , 张艳 , 罗渝昆 . 超声高清微血流成像技术在鉴别乳腺良恶性结节中的应用价值[J]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2023 , 20(12) : 1242 -1247 . DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2023.12.004
To evaluate the value of ultrasonic high-definition micro-flow imaging (HD-MFI) in differentiating benign and malignant breast masses.
This was a prospective study in which all the patients were enrolled from the First Medical Center, Chinese PLA General Hospital from March 2022 to June 2022, with all masses classified as breast imaging reporting and data system (BI-RADS) 3-5 categories and confirmed by pathology. The blood flow of all masses was evaluated by color Doppler flow imaging (CDFI) and HD-MFI, respectively, and the microvascular patterns (avascular, linear, tree-like, root hair-like, and crab claw-like) of all the masses were assessed by HD-MFI. The detection of blood flow between benign and malignant masses by CDFI and HD-MFI was compared respectively, as well as the differences in microvascular patterns detected by HD-MFI. The diagnostic efficacy of CDFI and HD-MFI in the diagnosis of breast masses was assessed and compared by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
A total of 114 patients with 119 breast masses were enrolled in this study, and there were 71 benign and 48 malignant masses. More Alder's grade 3 blood flow signals were detected by HD-MFI than by CDFI (72.3% vs 20.1%). On HD-MFI, both benign and malignant breast masses were mostly displayed as Alder's grades 2 and 3, and the proportion of grade 3 malignancies was higher than that of benign masses (85.4% vs 63.4%, P<0.05). Avascular, line-like, and tree-like microvascular patterns were more frequently seen in benign masses by HD-MFI, while root hair-like and crab claw-like patterns were more frequent in malignant masses (P<0.05). The diagnostic specificity (91.5% vs 81.7%), accuracy (86.6% vs 82.4%), positive predictive value (PPV) (86.4% vs 75.5%), and area under the curve [0.854 (0.777~0.912) vs 0.825 (0.745~0.889)] of HD-MFI were higher than those of CDFI.
HD-MFI is a more sensitive technique in detecting blood flow of breast masses in comparison with CDFI. HD-MFI could provide more blood flow information in differentiating benign and malignant breast masses through microvascular patterns.
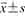 表示,组间比较采用独立样本t检验,计数资料以例(%)表示,组间比较采用χ2检验或Fisher精确检验以及多重比较Bonferroni法。以病理结果作为金标准,通过ROC曲线分别计算CDFI与HD-MFI诊断乳腺结节良恶性的敏感度、特异度、阳性预测值、阴性预测值和曲线下面积。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
表示,组间比较采用独立样本t检验,计数资料以例(%)表示,组间比较采用χ2检验或Fisher精确检验以及多重比较Bonferroni法。以病理结果作为金标准,通过ROC曲线分别计算CDFI与HD-MFI诊断乳腺结节良恶性的敏感度、特异度、阳性预测值、阴性预测值和曲线下面积。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。表1 乳腺良性与恶性结节的一般资料及常规超声特征比较 |
| 基本资料 | 良性结节(n=71) | 恶性结节(n=48) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
年龄[岁,(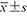 )] )] | 41.51±11.12 | 52.81±11.88 | t=-5.291 | <0.001 |
结节大小[cm,(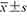 )] )] | 1.52±0.90 | 2.27±1.83 | t=-2.613 | 0.011 |
| 形态 [例(%)] | χ2=16.191 | <0.001 | ||
| 规则 | 36(50.7) | 7(14.6) | ||
| 不规则 | 35(49.3) | 41(85.4) | ||
| 边缘 [例(%)] | χ2=20.352 | <0.001 | ||
| 清晰 | 43(60.6) | 9(18.8) | ||
| 不清 | 28(39.4) | 39(81.2) | ||
| 纵横比 [例(%)] | χ2=8.960 | 0.003 | ||
| <1 | 66(93.0) | 35(72.9) | ||
| >1 | 5(7.0) | 13(27.1) | ||
| 回声 [例(%)] | χ2=3.762 | 0.152 | ||
| 低回声 | 66(93.0) | 44(91.7) | ||
| 囊实混合回声 | 3(4.2) | 0 | ||
| 实性不均回声 | 2(2.8) | 4(8.3) | ||
| 后方回声 [例(%)] | χ2=16.901 | <0.001 | ||
| 增强 | 12(16.9) | 9(18.8) | ||
| 衰减 | 16(22.5) | 27(56.3) | ||
| 无变化 | 43(60.6) | 12(25.0) | ||
| 钙化[例(%)] | χ2=11.345 | 0.003 | ||
| 无钙化 | 61(86.0) | 33(68.8) | ||
| 微钙化 | 5(7.0) | 14(29.2) | ||
| 粗大钙化 | 5(7.0) | 1(2.0) | ||
| BI-RADS分类 [例(%)] | χ2=62.392 | <0.001 | ||
| 3 | 3(4.2) | 0 | ||
| 4a | 55(77.5) | 8(16.7) | ||
| 4b | 12(16.9) | 21(43.8) | ||
| 4c | 1(1.4) | 11(22.9) | ||
| 5 | 0 | 8(16.7) |
注:BI-RADS为乳腺影像报告与数据系统 |
表2 CDFI与HD-MFI对乳腺结节进行Alder血流分级的结果比较[例(%)] |
| 检查方式 | 结节个数 | Alder血流分级 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0级 | 1级 | 2级 | 3级 | ||
| CDFI | 119 | 36(30.3) | 29(24.4) | 30(25.2) | 24(20.1) |
| HD-MFI | 119 | 6(5.0) | 10(8.4) | 17(14.3) | 86(72.3) |
| χ2值 | 69.226 | ||||
| P值 | <0.001 | ||||
注:CDFI为彩色多普勒血流成像;HD-MFI为高清微血流成像 |
表3 CDFI、HD-MFI检测的良性与恶性乳腺结节Alder血流分级比较[例(%)] |
| 结节性质 | 结节个数 | Alder血流分级 | 统计值 | P值 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0级 | 1级 | 2级 | 3级 | ||||
| CDFI | χ2=10.553 | 0.014 | |||||
| 良性 | 71 | 28(39.4) | 19(26.8) | 13(18.3) | 11(15.5) | ||
| 恶性 | 48 | 8(16.7) | 10(20.8) | 17(35.4) | 13(27.1) | ||
| HD-MFI | χ2=14.207 | 0.016 | |||||
| 良性 | 71 | 6(8.5) | 9(12.7) | 11(15.5) | 45(63.4) | ||
| 恶性 | 48 | 0 | 1(2.1) | 6(12.5) | 41(85.4) | ||
注:CDFI为彩色多普勒血流成像;HD-MFI为高清微血流成像 |
表4 良性与恶性乳腺结节的HD-MFI微血管模式比较[例(%)] |
| 结节性质 | 个数 | 微血管模式 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无血管 | 线样 | 树枝样 | 毛根样 | 蟹足样 | ||
| 良性 | 71 | 6(8.5) | 10(14.0) | 54(76.1) | 0 | 1(1.4) |
| 恶性 | 48 | 0 | 4(8.3) | 8(16.7) | 13(27.1) | 23(47.9) |
| χ2值 | 87.747 | |||||
| P值 | <0.001 | |||||
注:HD-MFI为高清微血流成像 |
图1 良性乳腺结节的彩色多普勒血流成像(CDFI)及高清微血流成像(HD-MFI)图像(患者,女性,48岁,左乳8点结节超声图像)。图a为常规二维超声图像;图b为CDFI提示结节内可见1级血流信号;图c为HD-MFI提示结节内可见3级血流信号,该结节微血管模式呈树枝样;术后病理提示乳腺腺病伴纤维腺瘤形成 |
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
秦菁, 马莉, 孝梦甦, 等. 老年女性乳腺癌的临床特征及超声诊断价值[J/OL]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2022, 19(2): 170-175.
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
黄碧霞, 甘小添, 廖红霞, 等. 微视血流成像技术检测乳腺良恶性肿物的应用价值[J]. 中外医学研究, 2021, 19(13): 70-72.
|
| 11 |
张小玲, 王丽梅, 黎晴. 微视血流成像技术在乳腺肿物良恶性鉴别中的应用价值[J]. 影像研究与医学应用, 2021, 5(23): 204-206.
|
| 12 |
宋青, 康林立, 兰雨, 等. 微血流成像模式鉴别甲状腺结节良恶性的价值[J]. 中国医学科学院学报, 2022, 44(1): 40-44.
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |