

2024 , Vol. 21 >Issue 01: 57 - 62
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2024.01.009
BRAF V600E基因及ACR TI-RADS分类对Bethesda Ⅲ类甲状腺结节风险评估价值
Copy editor: 吴春凤
收稿日期: 2023-03-11
网络出版日期: 2024-03-27
版权
Value of BRAF V600E mutation and ACR TI-RADS classification in risk assessment of Bethesda Ⅲ thyroid nodules
Received date: 2023-03-11
Online published: 2024-03-27
Copyright
探究BRAF V600E基因和美国放射学会(ACR)甲状腺影像报告和数据系统(TI-RADS)分类对Bethesda Ⅲ类甲状腺结节的风险评估价值。
回顾性分析2019年4月至2022年4月在中日友好医院行超声引导下细针穿刺细胞学检查且有手术病理结果的Bethesda Ⅲ类结节127个,根据病理结果将结节分为良性组(19个)和恶性组(108个)。采用χ2检验比较Bethesda Ⅲ类结节良、恶性组BRAF基因检测结果及ACR TI-RADS分类差异,比较2种方法单独及联合对Bethesda Ⅲ类结节的诊断效能,并用BRAF基因和ACR TI-RADS分类对Bethesda Ⅲ类结节进行恶性风险分层管理。
BRAF基因诊断Bethesda Ⅲ类结节的敏感度、特异度、准确性分别为47.2%、100%、55.1%,ACR TI-RADS分类的敏感度、特异度、准确性分别为81.5%、68.4%、79.5%,BRAF基因联合ACR TI-RADS分类的敏感度、特异度、准确性分别为92.6%、68.4%、89.0%,二者联合诊断的敏感度和准确性高于ACR TI-RADS分类,差异有统计学意义(χ2=10.08、4.27,P=0.002、0.039)。BRAF基因阳性的Bethesda Ⅲ类结节恶性率为100%,建议手术治疗。BRAF基因阴性Bethesda Ⅲ类结节中,ACR TI-RADS 3类结节恶性率为0,建议随访观察,ACR TI-RADS 4类结节恶性率为44.4%,建议重复穿刺活检,ACR TI-RADS 5类结节恶性率为89.1%,建议手术治疗。
BRAF V600E 基因联合ACR TI-RADS分类能够提高Bethesda Ⅲ类结节良恶性诊断的敏感度和准确性,能够实现对Bethesda Ⅲ类结节风险分层并指导临床处置。
刘健 , 谢尚宏 , 席雪华 , 张波 . BRAF V600E基因及ACR TI-RADS分类对Bethesda Ⅲ类甲状腺结节风险评估价值[J]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2024 , 21(01) : 57 -62 . DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2024.01.009
To evaluate the value of BRAF V600E mutation and American College of Radiology (ACR) thyroid imaging reporting and data system (TI-RADS) classification in risk assessment of Bethesda Ⅲ thyroid nodules.
A retrospective analysis was conducted on 127 Bethesda category Ⅲ nodules in patients who underwent fine needle aspiration cytology (FNA) and subsequent surgical pathology examination at China-Japan Friendship Hospital from April 2019 to April 2022. According to pathological findings, the nodules were divided into either a benign group (n=19) or a malignant group (n=108). The Chi-square test was used to compare the differences in the BRAF gene test results and ACR TI-RADS classification between benign and malignant groups of Bethesda category Ⅲ nodules. The diagnostic efficacy of BRAF gene mutation and ACR TI-RADS classification, individually and combined, for Bethesda category Ⅲ nodules was compared, and a malignancy risk stratification for Bethesda category Ⅲ nodules was performed using the BRAF gene muatation and ACR TI-RADS classification.
The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of BRAF V600E mutation for diagnosing Bethesda category Ⅲ nodules were 47.2%, 100%, and 55.1%, respectively. The corresponding values for ACR TI-RADS classification were 81.5%, 68.4%, and 79.5%, respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of BRAF V600E mutation combined with ACR TI-RADS classification were 92.6%, 68.4%, and 89.0%, respectively. The combined method showed statistically significant higher sensitivity and accuracy compared to ACR TI-RADS classification alone (χ2=10.08 and 4.27; P=0.002 and 0.039, respectively). Bethesda category Ⅲ nodules with positive BRAF gene results had a 100% risk of malignancy and were recommended for surgical treatment. For BRAF-negative Bethesda category Ⅲ nodules, those with ACR TI-RADS 3 classification had a 0% malignancy rate and were recommended for follow-up observation, ACR TI-RADS 4 nodules had a 44.4% malignancy rate and were suggested for repeat FNA, and ACR TI-RADS 5 nodules had an 89.1% malignancy rate and were recommended for surgical treatment.
The combination of BRAF V600E mutation with ACR TI-RADS classification improves the diagnostic sensitivity and accuracy for Bethesda category Ⅲ nodules and facilitates risk stratification and clinical management of these nodules.
Key words: Thyroid nodule; Ultrasound; BRAF gene; Risk assessment
 表示,良、恶性组间差异比较采用t检验;结节最大径为不符合正态分布的计量资料,采用M(QR)表示,组间差异比较用Mann-Whiney U检验。性别、位置、结构、回声、边缘、形态、钙化为计数资料,使用频数和百分率表示,组间差异比较采用χ2检验或Fisher确切概率法。ACR TI-RADS分类及联合法以5类为截断值,用χ2检验比较BRAF基因结果、ACR TI-RADS分类及联合法分类诊断Bethesda Ⅲ类结节良、恶性效能的差异。P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
表示,良、恶性组间差异比较采用t检验;结节最大径为不符合正态分布的计量资料,采用M(QR)表示,组间差异比较用Mann-Whiney U检验。性别、位置、结构、回声、边缘、形态、钙化为计数资料,使用频数和百分率表示,组间差异比较采用χ2检验或Fisher确切概率法。ACR TI-RADS分类及联合法以5类为截断值,用χ2检验比较BRAF基因结果、ACR TI-RADS分类及联合法分类诊断Bethesda Ⅲ类结节良、恶性效能的差异。P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。表1 Bethesda Ⅲ类结节良恶性组临床及超声特征比较 |
| 项目 | 恶性组(n=108) | 良性组(n=19) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[例(%)] | χ2=0.204 | 0.652 | ||
| 男 | 28(25.9) | 4(21.1) | ||
| 女 | 80(74.1) | 15(78.9) | ||
年龄(岁,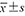 ) ) | 47±11 | 46±14 | t=0.512 | 0.610 |
| 位置[例(%)] | χ2=2.734 | 0.255 | ||
| 左叶 | 48(44.4) | 12(63.2) | ||
| 右叶 | 55(50.9) | 7(36.8) | ||
| 峡部 | 5(4.7) | 0(0) | ||
| 结节最大径[cm,M(QR)] | 0.7(0.5,1.0) | 0.8(0.5,1.7) | Z=-1.071 | 0.284 |
| 结构[例(%)] | χ2=0.177 | 0.674 | ||
| 实性 | 107(99.1) | 19(100) | ||
| 囊实性 | 1(0.9) | 0(0) | ||
| 回声[例(%)] | χ2=26.051 | <0.001 | ||
| 中等回声 | 2(1.9) | 6(31.6) | ||
| 低回声 | 89(82.4) | 13(68.4) | ||
| 极低回声 | 17(15.7) | 0(0) | ||
| 边缘[例(%)] | χ2=44.039 | <0.001 | ||
| 清晰 | 10(9.3) | 9(47.4) | ||
| 模糊 | 5(4.6) | 7(36.8) | ||
| 不规则或小分叶 | 88(81.5) | 3(15.8) | ||
| 腺体外侵犯 | 5(4.6) | 0(0) | ||
| 形态[例(%)] | χ2=3.436 | 0.064 | ||
| 纵横比≥1 | 59(54.6) | 6(31.6) | ||
| 纵横比<1 | 49(45.4) | 13(68.4) | ||
| 钙化[例(%)] | χ2=1.157 | 0.763 | ||
| 无钙化或大彗星尾征 | 52(48.1) | 10(52.6) | ||
| 粗大钙化 | 21(19.4) | 5(26.3) | ||
| 周边钙化 | 7(6.5) | 1(5.3) | ||
| 点状强回声 | 28(26.0) | 3(15.8) |
表2 Bethesda Ⅲ类结节良、恶性组应用BRAF基因、ACR TI-RADS分类及二者联合分类比较 |
| 组别 | 例数 | BRAF基因 | ACR TI-RADS分类 | 二者联合法 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阳性 | 阴性 | 3类 | 4类 | 5类 | 3类 | 4类 | 5类 | ||
| 良性组 | 19 | 0(0) | 19(100) | 3(15.8) | 10(52.6) | 6(31.6) | 13(68.4) | 0(0) | 6(31.6) |
| 恶性组 | 108 | 51(47.2) | 57(52.8) | 0(0) | 20(18.5) | 88(81.5) | 8(7.4) | 0(0) | 100(92.6) |
| χ2值 | 14.993 | 30.449 | 43.528 | ||||||
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||
注:TI-RADS为甲状腺影像和数据报告系统,ACR为美国放射学会 |
表3 BRAF基因、ACR TI-RADS分类及二者联合诊断效能比较(%) |
| 方法 | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 准确性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BRAF基因 | 47.2 | 100.0 | 55.1 |
| ACR TI-RADS分类 | 81.5 | 68.4 | 79.5 |
| 二者联合 | 92.6 | 68.4 | 89.0 |
| χ2值a | 21.25 | 4.17 | 17.20 |
| P值a | <0.001 | 0.041 | <0.001 |
| χ2值b | 47.02 | 4.17 | 38.63 |
| P值b | <0.001 | 0.041 | <0.001 |
| χ2值c | 10.08 | - | 4.27 |
| P值c | 0.002 | - | 0.039 |
注:TI-RADS为甲状腺影像和数据报告系统,ACR为美国放射学会;a为BRAF基因与TI-RADS分类比较的统计值,b为二者联合与BRAF基因比较的统计值,c为二者联合与TI-RADS分类比较的统计值;-表示无相应数据 |
表4 Bethesda Ⅲ类结节BRAF基因及ACR TI-RADS分类恶性风险[个(%)] |
| 病理 | 个数 | BRAF基因阳性 | BRAF基因阴性 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TI-RADS 3类 | TI-RADS 4类 | TI-RADS 5类 | TI-RADS 3类 | TI-RADS 4类 | TI-RADS 5类 | |||
| 恶性 | 108 | 0(0) | 12(100) | 39(100) | 0(0) | 8(44.4) | 49(89.1) | |
| 良性 | 19 | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 3(100) | 10(55.6) | 6(10.9) | |
注:TI-RADS为甲状腺影像和数据报告系统,ACR为美国放射学会 |
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
曹建辉, 黄伟伟, 潘敏强, 等. ACR TI-RADS与Kwak TI-RADS对甲状腺峡部结节的诊断价值 [J/OL]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2021, 18(2): 164-170.
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
王剑翔, 俞飞虹, 叶新华, 等. 超声联合BRAF V600E检测对BSRTC Ⅲ类甲状腺结节的诊断价值 [J/OL]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2020, 17(12): 1178-1182.
|
| 11 |
王也, 姜睿盈, 底锦熙, 等. RAS、BRAF、TERT基因在甲状腺细针穿刺样本中的表达特点 [J]. 诊断病理学杂志, 2020, 27(11): 769-774.
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |