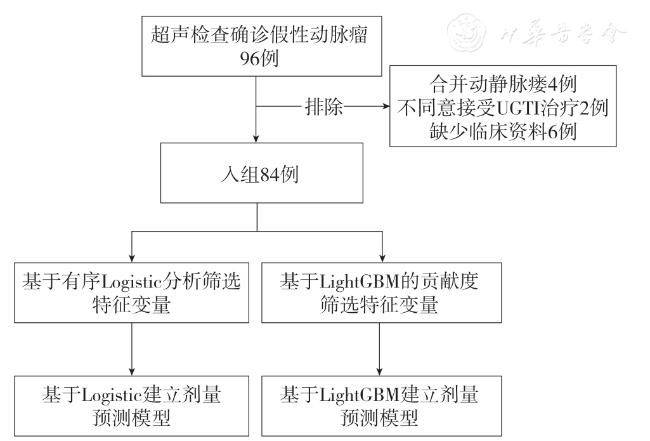
资料与方法
一、对象
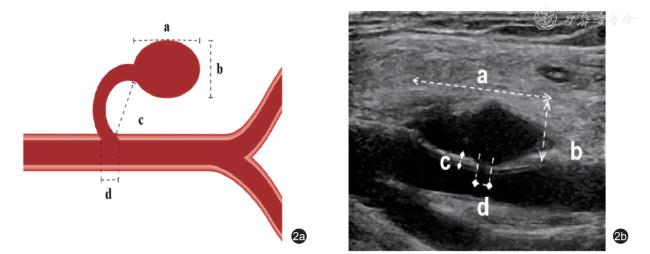
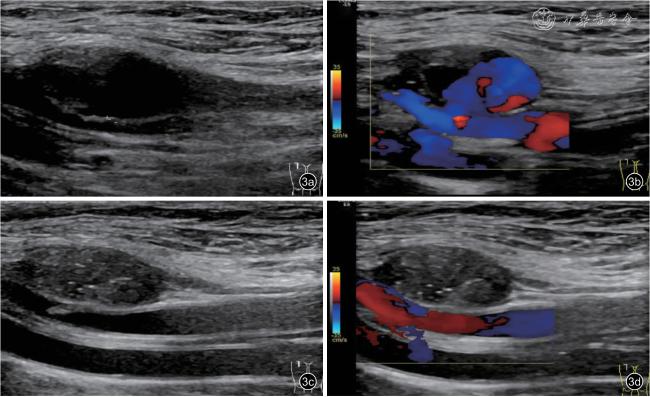
二、仪器与方法
三、数据处理及模型构建与评估
四、统计学分析
 ±s 表示,不同剂量组间比较采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)检验;不符合正态分布的计量资料采用M(Q1,Q3)表示,不同剂量组间比较采用Kruskal-Wallis 检验。计数资料采用例(%)表示,不同剂量组间比较根据样本量和理论频数选择χ2 检验或Fisher 精确检验。
±s 表示,不同剂量组间比较采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)检验;不符合正态分布的计量资料采用M(Q1,Q3)表示,不同剂量组间比较采用Kruskal-Wallis 检验。计数资料采用例(%)表示,不同剂量组间比较根据样本量和理论频数选择χ2 检验或Fisher 精确检验。五、数据可用性声明
结 果
一、患者基本信息
表1 假性动脉瘤患者训练集不同凝血酶剂量的3 组间临床资料比较 |
| 临床资料 | 低剂量(n=24) | 中剂量(n=26) | 高剂量(n=17) | 统计值 | P 值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 瘤腔长径(mm, ±s) | 21.89±8.69 | 27.83±9.09 | 37.17±11.13 | F=12.86 | < 0.001 |
| 瘤腔短径(mm, ±s) | 13.06±5.94 | 15.85±4.77 | 18.42±5.24 | F=5.11 | 0.009 |
| 浓度[IU/ml,M( Q1,Q3)] | 500.00(400.00,541.67) | 500.00(500.00,500.00) | 500.00(500.00,500.00) | Z=2.33 | 0.312 |
| 年龄[ 岁,M( Q1,Q3)] | 62.00(56.00,68.00) | 60.50(55.50,67.00) | 63.00(58.00,72.00) | Z=1.05 | 0.591 |
| 瘘管长度[mm,M( Q1,Q3)] | 4.00(2.08,10.46) | 2.55(2.02,4.90) | 2.90(1.70,7.40) | Z=3.93 | 0.140 |
| 破口内径[mm,M( Q1,Q3)] | 2.10(1.65,2.85) | 2.10(1.64,2.80) | 2.20(1.80,3.00) | Z=0.54 | 0.762 |
| PSV[cm/s,M( Q1,Q3)] | 170.95(118.75,300.00) | 195.00(109.00,296.27) | 201.10(170.00,250.00) | Z=0.27 | 0.873 |
| PT[s,M( Q1,Q3)] | 11.80(11.67,16.18) | 12.65(11.60,14.80) | 12.70(11.70,13.90) | Z=0.03 | 0.984 |
| INR[M( Q1,Q3)] | 1.02(1.01,1.31) | 1.10(1.01,1.31) | 1.11(1.02,1.22) | Z=0.42 | 0.809 |
| APTT[s,M( Q1,Q3)] | 30.20(27.65,35.38) | 30.20(27.27,34.70) | 29.40(27.80,33.20) | Z=0.04 | 0.981 |
| FIB[g/L,M( Q1,Q3)] | 2.56(2.11,3.53) | 2.44(2.15,3.04) | 2.83(2.38,3.08) | Z=1.28 | 0.527 |
| TT[s,M( Q1,Q3)] | 17.25(16.75,17.72) | 17.30(16.65,18.05) | 17.90(17.30,18.30) | Z=4.54 | 0.103 |
| DD2[mg/L,M( Q1,Q3)] | 0.27(0.15,0.47) | 0.33(0.13,1.18) | 0.19(0.12,0.24) | Z=2.69 | 0.261 |
| 性别[ 例(%)] | χ 2=0.62 | 0.735 | |||
| 男 | 14(58.33) | 15(57.69) | 8(47.06) | ||
| 女 | 10(41.67) | 11(42.31) | 9(52.94) | ||
| 抗凝药[ 例(%)] | - | 0.761 | |||
| 未使用 | 11(45.83) | 13(50.00) | 6(35.29) | ||
| 使用1 种 | 12(50.00) | 13(50.00) | 10(58.82) | ||
| 使用2 种 | 1(4.17) | 0(0.00) | 1(5.88) | ||
| 抗血小板药[ 例(%)] | - | 0.996 | |||
| 未使用 | 12(50.00) | 14(53.85) | 9(52.94) | ||
| 使用1 种 | 7(29.17) | 7(26.92) | 4(23.53) | ||
| 使用2 种 | 5(20.83) | 5(19.23) | 4(23.53) | ||
| 高血压[ 例(%)] | χ 2=0.31 | 0.855 | |||
| 否 | 10(41.67) | 10(38.46) | 8(47.06) | ||
| 是 | 14(58.33) | 16(61.54) | 9(52.94) |
注:PSV 为破口处峰值流速;PT 为凝血酶原时间;INR 为国际标准化比值;APTT 为活化部分凝血活酶时间;FIB 为纤维蛋白原;TT 为凝血酶时间;DD2 为D-二聚体;-为Fisher 检验无统计值 |
二、构建Logistic 凝血酶剂量预测模型
表2 假性动脉瘤患者凝血酶使用剂量影响因素的有序Logistic 回归分析 |
| 参数 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ 2 值 | P 值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | |||||
| 男性 | 1.00(Reference) | ||||
| 女性 | 0.30 | 0.46 | 0.66 | 0.510 | 1.35(0.55 ~ 3.30) |
| 抗凝药物 | |||||
| 不使用 | 1.00(Reference) | ||||
| 使用1 种 | 0.25 | 0.46 | 0.54 | 0.592 | 1.28(0.52 ~ 3.14) |
| 使用2 种 | 0.38 | 1.57 | 0.24 | 0.808 | 1.47(0.07 ~ 32.14) |
| 抗血小板药物 | |||||
| 不使用 | 1.00(Reference) | ||||
| 使用1 种 | -0.19 | 0.54 | -0.36 | 0.718 | 0.82(0.29 ~ 2.36) |
| 使用2 种 | 0.03 | 0.59 | 0.05 | 0.962 | 1.03(0.32 ~ 3.26) |
| 高血压 | |||||
| 无 | 1.00(Reference) | ||||
| 有 | -0.13 | 0.46 | -0.27 | 0.784 | 0.88(0.36 ~ 2.17) |
| 浓度 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -0.13 | 0.489 | 1.00(1.00 ~ 1.00) |
| 年龄 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.820 | 1.00(0.97 ~ 1.04) |
| 瘤腔长径 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 4.18 | <0.001 | 1.12(1.06 ~ 1.18) |
| 瘤腔短径 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 3.04 | <0.001 | 1.15(1.05 ~ 1.25) |
| 破口内径 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.66 | 0.512 | 1.16(0.75 ~ 1.80) |
| 瘘管长度 | -0.02 | 0.04 | -0.71 | 0.475 | 0.98(0.91 ~ 1.04) |
| PSV | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.863 | 1.00(1.00 ~ 1.00) |
| PT | -0.03 | 0.03 | -1.16 | 0.247 | 0.97(0.92 ~ 1.02) |
| INR | -0.14 | 0.41 | -0.33 | 0.741 | 0.87(0.39 ~ 1.96) |
| APTT | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.974 | 1.00(0.98 ~ 1.02) |
| FIB | -0.06 | 0.27 | -0.22 | 0.829 | 0.94(0.55 ~ 1.61) |
| DD2 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.94 | 0.350 | 1.18(0.84 ~ 1.66) |
| TT | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.92 | 0.359 | 1.01(0.99 ~ 1.04) |
注:PSV 为破口处峰值流速;PT 为凝血酶原时间;INR 为国际标准化比值;APTT 为活化部分凝血活酶时间;FIB 为纤维蛋白原;TT 为凝血酶时间;DD2 为D-二聚体 |
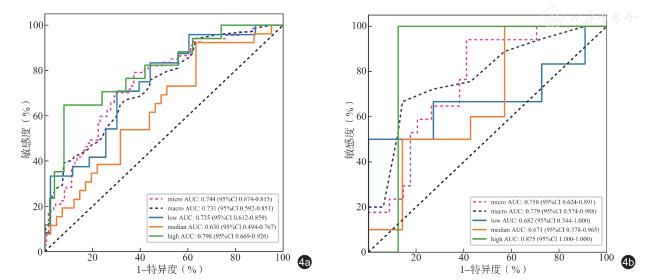
表3 Logistic 凝血酶剂量预测模型在训练集和验证集的诊断性能比较 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 准确性 | AUC | 95%CI | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 阳性预测值 | 阴性预测值 | 精确度 | 召回率 | F1 分数 | 阈值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 训练集 | 67 | 0.677 | 0.744 | 0.674 ~ 0.815 | 0.776 | 0.627 | 0.510 | 0.848 | 0.510 | 0.776 | 0.615 | 0.365 |
| 验证集 | 17 | 0.686 | 0.758 | 0.624 ~ 0.891 | 0.882 | 0.588 | 0.517 | 0.909 | 0.517 | 0.882 | 0.652 | 0.295 |
注:AUC 为曲线下面积;CI 为置信区间;表格中结果均为微平均值 |
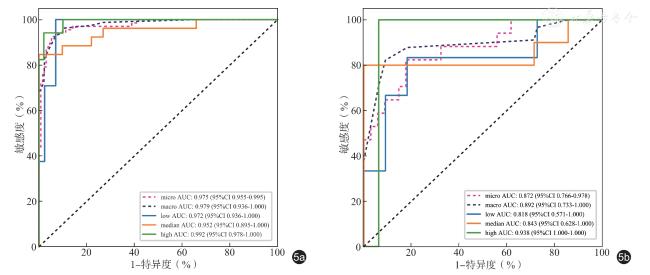
三、构建LightGBM 凝血酶剂量预测模型
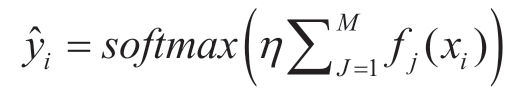
 是样本xi 的预测概率分布;η=0.1 为学习率;f j( xi)是在第j 棵树的输出;M=100为树的总数。
是样本xi 的预测概率分布;η=0.1 为学习率;f j( xi)是在第j 棵树的输出;M=100为树的总数。表4 LightGBM 凝血酶剂量预测模型在训练集和验证集的诊断性能比较 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 准确性 | AUC | 95%CI | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 阳性预测值 | 阴性预测值 | 精确度 | 召回率 | F1 分数 | 阈值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 训练集 | 67 | 0.930 | 0.975 | 0.955 ~ 0.995 | 0.925 | 0.933 | 0.873 | 0.962 | 0.873 | 0.925 | 0.899 | 0.353 |
| 验证集 | 17 | 0.804 | 0.872 | 0.766 ~ 0.978 | 0.765 | 0.824 | 0.684 | 0.875 | 0.684 | 0.765 | 0.722 | 0.359 |
注:AUC 为曲线下面积;CI 为置信区间;表格中结果均为微平均值 |