

2023 , Vol. 20 >Issue 12: 1294 - 1299
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2023.12.013
不同超声治疗时间激励微泡空化对肿瘤血流灌注的影响
Copy editor: 汪荣
收稿日期: 2023-02-05
网络出版日期: 2024-03-05
版权
Effect of treatment with ultrasound-stimulated microbubbles for different durations on tumor blood perfusion in mice
Received date: 2023-02-05
Online published: 2024-03-05
Copyright
探讨不同超声治疗时间对超声激励微泡空化增强小鼠MC38肿瘤血流灌注的影响,并对机制进行初步分析。
选取54只大腿内侧皮下种植MC38的荷瘤小鼠,利用飞依诺超声诊疗一体机Vflash模式激励微泡空化行超声治疗(MI=0.3)。小鼠按超声治疗时间(t)随机分为6组(n=9):A组,t=1 min;B组,t=3 min;C组,t=5 min;D组,t=7 min;E组,t=10 min;F组(对照组),不接受超声治疗。每组治疗前后分别行超声造影检查,通过治疗前后峰值强度(PI)比、曲线下面积(AUC)比及肿瘤血流灌注面积比综合评估肿瘤血流灌注情况。治疗后,每组随机取2只小鼠肿瘤组织进行HE染色,观察治疗后病理学改变;取各组余下的7只小鼠肿瘤组织进行一氧化氮含量测定。
超声激励微泡空化治疗后,C、D、E组治疗前后PI比、AUC比及灌注面积比均明显高于对照组(P均<0.05);其中D组治疗前后PI比、AUC比最高,明显高于C组(P<0.05)、B组(P<0.05)、A组(P<0.01),灌注面积比高于A组(P<0.01)、B组(P<0.05)。病理结果显示C、D、E组肿瘤微血管扩张充血,其中D组扩张微血管数量最多,充血最明显。超声治疗的各组肿瘤组织内一氧化氮含量较对照组增加,其中D组一氧化氮含量最高,但各组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
超声激励微泡空化可以增强小鼠MC38肿瘤血流灌注,超声治疗时间延长到5 min以上,肿瘤血流增强效果更加明显;超声治疗7 min时,超声肿瘤血流效应最为明显。其机制可能与超声激励微泡空化导致微血管扩张有关。
张静 , 张毅 , 蔡治平 , 魏俊帅 , 刘政 . 不同超声治疗时间激励微泡空化对肿瘤血流灌注的影响[J]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2023 , 20(12) : 1294 -1299 . DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2023.12.013
To investigate the effect of treatment with ultrasound-stimulated microbubbles (USMB) for different durations in enhancing blood perfusion in MC38 tumors in mice, and to analyze the underlying mechanism preliminarily.
A total of 54 tumor-bearing mice with MC38 tumor cells implanted subcutaneously on the inner thigh were selected and treated by microbubble cavitation stimulated using the VINNO US system in Vflash mode (mechanical index=0.3). The mice were randomly divided into 6 groups according to the treatment duration, with 9 mice in each group: Group A, t=1 min; Group B, t=3 min; Group C, t=5 min; Group D, t=7 min; Group E, t=10 min; Group F (control group), no ultrasound therapy. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound examinations were performed before and after treatment for each group, and tumor perfusion was evaluated comprehensively by peak intensity (PI) ratio, area under curve (AUC) ratio, and tumor perfusion area ratio before and after treatment.Two mice in each group were randomly selected to take tumor tissues for HE staining to observe the pathological changes after treatment. The remaining 7 mice in each group were collected for the determination of nitric oxide (NO) content.
After ultrasonic stimulation, the PI ratio, AUC ratio, and perfusion area ratio in Groups C, D, and E were significantly higher than those of the control group (P<0.05). Group D had the highest PI ratio and AUC ratio, which were significantly higher than those of Groups C (P<0.05), B (P<0.05), and A (P<0.01), and the perfusion area ratio in Group D was higher than those of Groups A (P<0.01) and B (P<0.05). The pathological results showed that the tumor microvessels in Groups C, D, and E were dilated and congested, with the number of dilated microvessels being most and congestion being most obvious in group D. The content of NO in tumor tissues of each group undergoing ultrasound therapy was higher than that of the control group. The content of NO in group D was the highest, but there was no significant difference among the groups (P>0.05).
Ultrasound-stimulated microbubbles can enhance blood perfusion of MC38 tumors in mice, and the enhancement effect is more obvious when the ultrasound treatment time is extended to more than 5 minutes. The best enhancement effect of tumor blood flow can be achieved when the ultrasound treatment time is 7 minutes. The therapeutic mechanism may be related to microvascular dilatation caused by ultrasound-stimulated microbubbles.
Key words: Ultrasound; Microbubble; Cavitation; Tumor blood perfusion; Treatment time
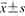 表示,不符合正态分布的以M(P25,P75)表示。各组PI比、AUC比、灌注面积比的比较采用单因素方差分析,组间两两比较采用LSD法;各组一氧化氮含量比较采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
表示,不符合正态分布的以M(P25,P75)表示。各组PI比、AUC比、灌注面积比的比较采用单因素方差分析,组间两两比较采用LSD法;各组一氧化氮含量比较采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。表1 各组小鼠超声治疗前后肿瘤血流效应分析( |
| 治疗前后比值 | A组 | B组 | C组 | D组 | E组 | F组 | F值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI比 | 1.01±0.06d | 1.03±0.09d | 1.05±0.08df | 1.13±0.07 | 1.06±0.05f | 0.97±0.05d | 4.99 | 0.001 |
| AUC比 | 1.03±0.08d | 1.05±0.12d | 1.07±0.09df | 1.15±0.06 | 1.08±0.07f | 0.99±0.05d | 4.03 | 0.004 |
| 血流灌注面积比 | 1.04±0.06cd | 1.06±0.08d | 1.12±0.11f | 1.15±0.10f | 1.11±0.09f | 0.99±0.06 | 3.99 | 0.004 |
注:PI为峰值强度;AUC为曲线下面积;A~E组分别为接受超声治疗1、3、5、7、10 min组;F组为未接受超声治疗组;与C组比较,cP<0.05;与D组比较,dP<0.05;与F组比较,fP<0.05 |
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
唐娜娇, 唐家伟, 张毅, 等. 微泡超声空化增强乏血供肿瘤血流灌注的实验研究[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2021, 30(2): 167-172.
|
| 8 |
乔学研, 陈重, 益磋, 等. 诊断超声联合微泡对兔VX_2肿瘤的血流增强效应[J]. 临床超声医学杂志, 2017, 19(4): 217-221.
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
王亚辉, 益磋, 冯爽, 等. 诊断超声产生的血流增强效应及肿瘤释药研究[J/CD]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2018, 15(4): 303-308.
|
| 12 |
张毅, 冯爽, 唐娜娇, 等. 超声诊疗一体机VINNO 70空化调控功能及声学测量的研究[J]. 临床超声医学杂志, 2021, 23(3): 161-165.
|
| 13 |
白露华, 罗婷婷, 唐家伟, 等. 不同超声脉冲宽度和脉冲重复频率组合激励微泡空化对肿瘤血流灌注及释药的影响[J]. 陆军军医大学学报, 2022, 44(9): 935-942.
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
姚雷, 杨国良, 殷佳蓓, 等. 不同占空比低强度诊断超声联合微泡对大鼠乏血供肿瘤血流灌注影响的实验研究[J]. 临床超声医学杂志, 2022, 24(8): 561-566.
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |