

2024 , Vol. 21 >Issue 07: 664 - 670
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2024.07.004
四川省超声医学质量控制指标动态变化趋势分析
Copy editor: 吴春凤
收稿日期: 2024-05-21
网络出版日期: 2024-07-09
基金资助
四川省自然科学基金(2022NSFSC0605)
版权
Dynamic changing trends of ultrasound medicine quality control indicators in Sichuan Province
Received date: 2024-05-21
Online published: 2024-07-09
Copyright
揭示2020—2022年四川省超声医学质量关键指标动态变化趋势和特征。
基于四川省医疗质控数据上报平台,收集并分析2020—2022年期间四川省21个市州超声质量管理控制指标数据,采用方差分析或非参数检验比较结构、过程、结果质量分析指标的差异。
2020—2022年四川省省域各市州三级专科医院医患比逐年下降[(1.75±0.93)人/万人次vs (1.59±0.55)人/万人次vs (1.49±0.56)人/万人次],超声医师月均工作量均逐年增加[(770.42±258.30)人/人次vs (965.73±323.52)人/人次vs (974.75±335.51)人/人次],超声诊断符合率逐年提高[(0.79±0.20)% vs (0.95±0.04)% vs (0.96±0.03)%],差异均具有统计学意义(F=4.11,P=0.020;F=3.74,P=0.040;F=7.39,P<0.001);三级综合、二级综合和二级专科医院间差异无统计学意义(P均>0.05)。各市州三级综合医院住院超声检查48 h内完成率逐年提高[1.00(0.98,1.00)% vs 1.00(0.99,1.00)% vs 1.00(0.97,1.00)%],差异具有统计学意义(H=6.73,P=0.035);三级专科、二级综合、二级专科医院差异无统计学意义(P均>0.05)。逐年比较,2020年四川省21个市州13个核心超声质控指标中医患比、医师月均工作量、门急诊超声报告阳性率、超声诊断符合率4个超声质控指比较,差异均具有统计学意义(P均<0.05);2021年医患比、门急诊超声报告阳性率、超声诊断符合率3个超声质控指标比较,差异仍具有统计学意义(P均<0.05);2022年仅超声诊断符合率1个超声质控指标差异具有统计学意义(P均<0.05),差异指标逐年减少。
2020—2022年四川省不同市州超声医学质量控制指标不断趋同,关键指标持续提升改进。
周易 , 张红梅 , 尹立雪 , 杨浩 , 付培 . 四川省超声医学质量控制指标动态变化趋势分析[J]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2024 , 21(07) : 664 -670 . DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2024.07.004
To reveal the dynamic changing trends and characteristics of key ultrasound medical quality control indicators in Sichuan Province from 2020 to 2022.
Based on the Sichuan Provincial Medical Quality Control Data Reporting Platform, we collected and analyzed data on ultrasound quality management control indicators in 21 cities or prefectures in Sichuan Province from 2020 to 2022. The basic situation of ultrasonographers in Sichuan Province as well as the structure, process, and outcome quality analysis indicators was analysed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) or non-parametric tests.
From 2020 to 2022, the average monthly workload of ultrasound physicians and the accuracy rate of ultrasound diagnosis in tertiary specialized hospitals in all cities and prefectures increased year by year, and the doctor-patient ratio in ultrasound departments decreased year by year, with the differences being statistically significant [1.75±0.93 vs 1.59±0.55 vs 1.49±0.56, F=4.11, P=0.020; 770.42±258.30 vs 965.73±323.52 vs 974.75±335.51, F=3.74, P=0.040; (0.79±0.20)% vs (0.95±0.04)% vs (0.96±0.03)%, F=7.39, P<0.001]; in contrast, there was no statistically significant difference in the above indicators in tertiary general hospitals, secondary general hospitals, and secondary specialized hospitals (P>0.05). The completion rate of ultrasound examinations within 48 hours of admission in tertiary general hospitals of all cities and prefectures increased significantly [1.00(0.98, 1.00)% vs 1.00(0.99, 1.00)% vs 1.00(0.97, 1.00)%, H=6.73, P=0.035], but there was no statistically significant difference in tertiary specialized hospitals, secondary general hospitals, and secondary specialized hospitals (P>0.05). When comparing 13 ultrasound quality control indicators in hospitals from 21 cities and prefectures in Sichuan Province in 2020, there were statistically significant differences in four ultrasound quality control indicators: doctor-patient ratio, average monthly workload of ultrasound physicians, positive rate of outpatient and emergency ultrasound reports, and ultrasound diagnostic coincidence rate (P<0.05 for all). In 2021, there were statistically significant differences in three ultrasound quality control indicators: doctor-patient ratio, positive rate of outpatient and emergency ultrasound reports, and ultrasound diagnostic accuracy (P<0.05 for all). However, in 2022, only one ultrasound quality control indicator, ultrasound diagnostic coincidence rate, had a statistically significant difference (P<0.05).
In recent years, the quality control indicators of ultrasound medicine in different cities and prefectures in Sichuan Province have been converging, and the key indicators have been continuously upgraded and improved.
Key words: Ultrasound medicine; Quality control; Management
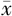 ±s表示,非正态分布的计量资料采用M(QR)表示。2020—2022年四川省超声医师基本情况(学历、年龄)为计数资料,采用百分率表示,采用χ2检验比较2020—2022年3年间和不同等级医院间的差异。四川省超声结构质量分析指标(超声仪器质检率)、4项超声过程质量分析指标(住院超声检查48 h内完成率、超声危急值10 min内通报完成率、超声报告书写合格率、BI-RADS分类率)、1项超声结构质量分析指标(超声筛查中胎儿重大致死性畸形检出率)为非正态分布计量资料,采用Kruskal-Wallis非参数检验比较多组间的差异。超声科医患比、超声医师月均工作量、门急诊超声报告阳性率、住院超声报告阳性率、超声诊断符合率为正态分布计量资料,若方差齐性,采用单因素方差分析比较多组间的差异,若方差不齐,采用Kruskal-Wallis非参数检验比较多组间的差异。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
±s表示,非正态分布的计量资料采用M(QR)表示。2020—2022年四川省超声医师基本情况(学历、年龄)为计数资料,采用百分率表示,采用χ2检验比较2020—2022年3年间和不同等级医院间的差异。四川省超声结构质量分析指标(超声仪器质检率)、4项超声过程质量分析指标(住院超声检查48 h内完成率、超声危急值10 min内通报完成率、超声报告书写合格率、BI-RADS分类率)、1项超声结构质量分析指标(超声筛查中胎儿重大致死性畸形检出率)为非正态分布计量资料,采用Kruskal-Wallis非参数检验比较多组间的差异。超声科医患比、超声医师月均工作量、门急诊超声报告阳性率、住院超声报告阳性率、超声诊断符合率为正态分布计量资料,若方差齐性,采用单因素方差分析比较多组间的差异,若方差不齐,采用Kruskal-Wallis非参数检验比较多组间的差异。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。表1 2020—2022年四川省不同等级医院部分超声质控指标比较 |
| 医院级别 | 数量 | 超声科医患比(人/万人次) | 住院超声检查48 h内完成率(%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020年 | 2021年 | 2022年 | F值 | P值 | 2020年 | 2021年 | 2022年 | H值 | P值 | ||
| 三级综合 | 112 | 1.54±1.02 | 1.51±1.49 | 1.32±0.50 | 1.72 | 0.180 | 1.00(0.98,1.00) | 1.00(0.99,1.00) | 1.00(0.97,1.00) | 6.73 | 0.035 |
| 三级专科 | 53 | 1.75±0.93 | 1.59±0.55 | 1.49±0.56 | 4.11 | 0.020 | 1.00(1.00,1.00) | 1.00(1.00,1.00) | 1.00(1.00,1.00) | 0.14 | 0.935 |
| 二级综合 | 65 | 2.11±1.11 | 2.30±1.40 | 2.05±1.16 | 0.93 | 0.398 | 1.00(0.99,1.00) | 1.00(0.99,1.00) | 1.00(0.95,1.00) | 0.48 | 0.787 |
| 二级专科 | 42 | 2.23±0.81 | 2.11±1.01 | 2.31±1.11 | 0.36 | 0.698 | 1.00(1.00,1.00) | 1.00(1.00,1.00) | 1.00(1.00,1.00) | 4.39 | 0.111 |
| 医院级别 | 数量 | 超医师月均工作量(人/人次) | 超声诊断符合率(%) | ||||||||
| 2020年 | 2021年 | 2022年 | F值 | P值 | 2020年 | 2021年 | 2022年 | F值 | P值 | ||
| 三级综合 | 112 | 1005.92±420.72 | 930.46±480.82 | 1027.89±437.53 | 2.45 | 0.092 | 0.88±0.11 | 0.92±0.07 | 0.92±0.08 | 2.46 | 0.092 |
| 三级专科 | 53 | 770.42±258.30 | 965.73±323.52 | 974.75±335.51 | 3.74 | 0.040 | 0.79±0.20 | 0.95±0.04 | 0.96±0.03 | 7.39 | <0.001 |
| 二级综合 | 65 | 726.48±384.11 | 735.95±325.83 | 801.26±398.66 | 0.97 | 0.379 | 0.82±0.11 | 0.84±0.25 | 0.89±0.08 | 0.31 | 0.743 |
| 二级专科 | 42 | 625.53±260.30 | 796.78±132.31 | 587.65±317.73 | 0.47 | 0.629 | 0.89±0.10 | 0.91±0.17 | 0.95±0.05 | 0.38 | 0.691 |
图3 2020—2022年四川省各市州超声科医患比变化注:2020年、2021年21个市州超声科医患比比较,差异具有统计学意义(F=2.83,P<0.001;F=2.49,P<0.001);2022年21个州市比较,差异无统计学意义(F=0.82,P=0.650) |
图4 2020—2022年四川省各市州超声医师月均工作量变化注:2020年21个市州超声医师月均工作量比较,差异具有统计学意义(F=2.61,P<0.001);2021年和2022年21个市州超声医师月均工作量比较,差异无统计学意义(F=1.21,P=0.23;F=1.20,P=0.27) |
表2 2020—2022年四川省各市州门急诊超声报告阳性率和超声诊断符合率变化(%) |
| 州市 | 门急诊超声报告阳性率 | 超声诊断符合率 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020年 | 2021年 | 2022年 | 2020年 | 2021年 | 2022年 | ||
| 成都市 | 0.75±0.14 | 0.74±0.21 | 0.76±0.15 | 0.86±0.10 | 0.92±0.08 | 0.91±0.09 | |
| 阿坝藏族羌族自治州 | 0.71±0.20 | 0.77±0.18 | 0.78±0.13 | 0.70±0.09 | 0.78±0.20 | 0.91±0.02 | |
| 巴中市 | 0.83±0.13 | 0.79±0.10 | 0.77±0.15 | 0.86±0.07 | 0.93±0.03 | 0.88±0.09 | |
| 达州市 | 0.65±0.24 | 0.66±0.24 | 0.69±0.28 | 0.80±0.20 | 0.84±0.15 | 0.84±0.16 | |
| 德阳市 | 0.73±0.15 | 0.64±0.24 | 0.71±0.06 | 0.92±0.03 | 0.95±0.04 | 0.97±0.03 | |
| 甘孜藏族自治州 | 0.68±0.20 | 0.54±0.37 | 0.69±0.21 | 0.66±0.19 | 0.80±0.20 | 0.96±0.04 | |
| 广安市 | 0.69±0.20 | 0.68±0.26 | 0.73±0.17 | 0.78±0.13 | 0.84±0.16 | 0.90±0.10 | |
| 广元市 | 0.83±0.13 | 0.76±0.18 | 0.84±0.15 | 0.90±0.05 | 0.92±0.08 | 0.92±0.08 | |
| 乐山市 | 0.81±0.13 | 0.77±0.18 | 0.82±0.14 | 0.91±0.06 | 0.92±0.07 | 0.93±0.05 | |
| 凉山彝族自治州 | 0.66±0.17 | 0.65±0.21 | 0.71±0.19 | 0.76±0.17 | 0.92±0.07 | 0.91±0.08 | |
| 泸州市 | 0.77±0.10 | 0.78±0.20 | 0.80±0.15 | 0.88±0.06 | 0.89±0.10 | 0.90±0.09 | |
| 眉山市 | 0.75±0.12 | 0.69±0.28 | 0.79±0.16 | 0.79±0.11 | 0.89±0.11 | 0.88±0.12 | |
| 绵阳市 | 0.75±0.14 | 0.71±0.22 | 0.72±0.20 | 0.87±0.09 | 0.90±0.10 | 0.94±0.05 | |
| 南充市 | 0.81±0.15 | 0.78±0.15 | 0.81±0.12 | 0.86±0.06 | 0.91±0.09 | 0.93±0.05 | |
| 内江市 | 0.81±0.12 | 0.69±0.30 | 0.75±0.12 | 0.88±0.05 | 0.88±0.12 | 0.91±0.07 | |
| 攀枝花市 | 0.89±0.08 | 0.83±0.13 | 0.87±0.09 | 0.91±0.05 | 0.91±0.06 | 0.92±0.04 | |
| 自贡市 | 0.79±0.16 | 0.78±0.15 | 0.75±0.16 | 0.84±0.07 | 0.95±0.04 | 0.93±0.04 | |
| 遂宁市 | 0.72±0.19 | 0.63±0.26 | 0.79±0.16 | 0.90±0.06 | 0.96±0.04 | 0.96±0.03 | |
| 雅安市 | 0.83±0.11 | 0.83±0.10 | 0.80±0.11 | 0.89±0.06 | 0.90±0.07 | 0.93±0.03 | |
| 宜宾市 | 0.79±0.15 | 0.72±0.24 | 0.75±0.11 | 0.88±0.08 | 0.92±0.07 | 0.74±0.23 | |
| 资阳市 | 0.70±0.15 | 0.79±0.11 | 0.70±0.23 | 0.89±0.03 | 0.93±0.07 | 0.94±0.05 | |
| F值 | 1.95 | 2.16 | 1.11 | 2.51 | 1.60 | 2.06 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.031 | 0.343 | <0.001 | 0.049 | 0.024 | |
| 1 |
国家卫生健康委员会. 《国家卫生健康委办公厅关于印发超声诊断等5个专业医疗质量控制指标(2022年版)的通知:国卫办医函(2022)161号 [EB/OL]. (2022-5-11)[2024-6-27].
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
谷杨, 王红燕, 李建初, 等. 超声医学相关质量指标的应用现状 [J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2019, 28(7): 639-641.
|
| 5 |
吕滨, 任心爽, 安云强, 等. 中国心血管影像技术应用现状调查与医疗质量报告 [J]. 中国循环杂志, 2020, 35(7): 625-633.
|
| 6 |
王佳佳, 王金萍, 姜凡, 等. 2019年度安徽省三级中医院和其他三级综合医院超声质量控制调查比较 [J/OL]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2021, 18(7): 643-646.
|
| 7 |
尹立雪, 张红梅. 超声医学质量控制的基本概念和基本原则 [J/OL]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2022, 19(7): 609-612.
|
| 8 |
郑宇觐, 刘会, 郭丹丹, 等. 标准化质量控制理念在超声医学科的应用研究 [J]. 协和医学杂志, 2023, 14(3): 575-580.
|
| 9 |
高璐滢, 王红燕, 谷杨, 等. 利用戴明循环法开展北京市超声医学质量控制的干预成效 [J/OL]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2021, 18(7): 647-651.
|
| 10 |
吕衡, 谢海琴, 陈香梅, 等. 随访数据信息化管理系统对超声医师诊断效能的影响 [J/OL]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2021, 18(8): 812-815.
|
| 11 |
李欣雨, 吴洋, 张红梅, 等. 深度学习技术在超声心动图图像质量控制中的应用 [J]. 实用医学杂志, 2024, 40(1): 108-113.
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
姜玉新. 信息化技术助力超声医学质量控制新发展 [J/OL]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2021, 18(7): 625-628.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |