

2024 , Vol. 21 >Issue 09: 884 - 889
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2024.09.008
机器人辅助超声引导下经皮穿刺的体外实验研究
Copy editor: 吴春凤
收稿日期: 2024-01-01
网络出版日期: 2024-10-16
版权
Ultrasound-guided robot-assisted percutaneous puncture: an experimental study
Received date: 2024-01-01
Online published: 2024-10-16
Copyright
目的
评估不同穿刺经验操作者在穿刺机器人辅助超声引导下经皮穿刺体外模型实验中的准确性和可行性。
方法
2 位不同年资的医师分别通过穿刺机器人辅助系统和徒手对甲状腺结节体模中的目标进行穿刺实验,每人分别做10 次穿刺。采用t 检验对比2 种穿刺方式的穿刺针尖定位误差、针轴角度误差以及操作时间的差异,并采用组内相关系数(ICC)分析不同年资医师使用穿刺机器人辅助系统进行穿刺实验的一致性。
结果
机器人辅助比徒手穿刺精准度更高,但操作时间更长,两者针尖定位误差为(0.62±0.26)mm vs (1.29±0.38)mm,针轴角度误差为(1.04±0.63)°vs (2.01±0.86)°,平均操作时间为(26.45±12.44)s vs (20.58±9.86)s,差异均具有统计学意义(t=9.187、P<0.001;t=3.409、P=0.003;t=-2.289、P=0.034)。不同经验的操作者利用机器人辅助系统穿刺,在针尖定位误差和操作时间上均具有极佳的一致性[ICC(95%可信区间)=0.783(0.126~0.946)、0.903(0.610~0.876)]。
结论
与徒手穿刺相比,使用机器人辅助系统穿刺具有更高的准确性及稳定性,但使用机器人辅助系统增加了操作时间。
孙佳丽 , 金琳 , 沈崔琴 , 陈晴晴 , 林艳萍 , 李朝军 , 徐栋 . 机器人辅助超声引导下经皮穿刺的体外实验研究[J]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2024 , 21(09) : 884 -889 . DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2024.09.008
Objective
To assess the accuracy and feasibility of ultrasound-guided robot-assisted percutaneous puncture.
Methods
Two physicians with different years of experience conducted ultrasound-guided puncture experiments on thyroid nodule phantoms using both the puncture robot-assisted system and manual puncture, each for 10 times. The puncture needle positioning error, directional error, and total operation time were recorded. Additionally, the consistency among physicians with different experience levels when using the puncture robot-assisted system for puncture was assessed.
Results
The robot-assisted group demonstrated higher puncture accuracy than the manual group, but with longer operation times. The average needle tip error in the robot-assisted group versus the manual group was (0.62±0.26) mm vs (1.29±0.38) mm, the average needle axis angle error was (1.04±0.63)° vs (2.01±0.86)°, and the average operation time was (26.45±12.44) s vs (20.58±9.86) s;the differences were statistically significant between the two groups ( t=9.187, P<0.001; t=3.409, P=0.003;t=-2.289, P=0.034). Operators with different experiences using the robot-assisted system for puncture showed good consistency in needle tip error and operation time, with intraclass correlation coefficient (95% confidence interval) values of 0.783 (0.126-0.946) and 0.903 (0.610-0.876), respectively (P<0.05).
Conclusion
Compared to manual puncture, the robot-assisted system exhibits higher accuracy and stability in ultrasound-guided thyroid nodule puncture procedures. However, the use of the robot-assisted system increases the operation time.
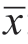 ±s 表示,采用配对t 检验比较徒手穿刺和机器人辅助穿刺时上述指标的差异;采用组内相关系数(intracluster correlation coefficient,ICC) 评估操作者间的一致性。根据常用标准将一致性分为极佳(ICC >0.75)、良好(ICC=0.60~0.75)、中等(ICC=0.40~0.59) 和较差(ICC<0.40)。 以P<0.05 为差异有统计学意义。
±s 表示,采用配对t 检验比较徒手穿刺和机器人辅助穿刺时上述指标的差异;采用组内相关系数(intracluster correlation coefficient,ICC) 评估操作者间的一致性。根据常用标准将一致性分为极佳(ICC >0.75)、良好(ICC=0.60~0.75)、中等(ICC=0.40~0.59) 和较差(ICC<0.40)。 以P<0.05 为差异有统计学意义。表1 使用机器人辅助系统和徒手穿刺的相关指标比较( |
| 穿刺方式 | 次数 | 针尖定位误差(mm) | 针轴角度误差(°) | 操作时间(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 徒手穿刺 | 20 | 1.29±0.38 | 2.01±0.86 | 20.58±9.86 |
| 机器人辅助 | 20 | 0.62±0.26 | 1.04±0.63 | 26.45±12.44 |
| t值 | 9.187 | 3.409 | -2.289 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.034 |
表2 不同经验操作者使用机器人辅助系统和徒手穿刺的相关指标比较( |
| 操作者 | 次数 | 针尖定位误差(mm) | 针轴角度误差(°) | 操作时间(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 操作者1 | ||||
| 徒手穿刺 | 10 | 1.37±0.34 | 2.00±0.79 | 20.43±8.64 |
| 机器人辅助 | 10 | 0.63±0.26 | 1.11±0.60 | 25.00±9.52 |
| t值 | 8.498 | 2.365 | -1.539 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.021 | 0.158 | |
| 操作者2 | ||||
| 徒手穿刺 | 10 | 1.22±0.42 | 2.02±0.97 | 20.73±11.44 |
| 机器人辅助 | 10 | 0.62±0.28 | 0.96±0.67 | 27.90±15.21 |
| t值 | 5.109 | 2.361 | -1.663 | |
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.021 | 0.131 |
| 1 |
Gharib H, Papini E, Paschke R, et al. American association of clinical endocrinologists, associazione medici endocrinologi, and european thyroid association medical guidelines for clinical practice for the diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules: Executive summary of recommendations [J]. J Endocrinol Invest, 2010, 33(5 Suppl): 51-56.
|
| 2 |
周乐, 付吉涛, 孙辉. 超声引导下细针穿刺技术在甲状腺外科中的应用进展 [J/OL]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2021, 18(9):895-897.
|
| 3 |
梁伟彬, 刘兴国, 何坚沃, 等. 术前细针穿刺活检在甲状腺手术中的应用 [J]. 中国药物经济学, 2018, 13(2): 3.
|
| 4 |
刘广华, 郑力鹏, 王瑞才, 等. 超声检查及引导细针穿刺活检在甲状腺结节良恶性中的鉴别诊断价值 [J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2023,33(5): 756-758.
|
| 5 |
刘冬, 孙斌, 杜宇, 等. 超声图像引导的机器人辅助定位系统设计与实验 [J]. 组合机床与自动化加工技术, 2022(9): 131-134.
|
| 6 |
成天佑, 林艳萍, 马晓军. 一种视触觉引导的超声探头自动定位方法 [J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2020, 47(1): 8.
|
| 7 |
Lau KC, Leung EYY, Chiu PWY, et al. A flexible surgical robotic system for removal of early-stage gastrointestinal cancers by endoscopic submucosal dissection [J]. IEEE Trans Industr Inform,2016, 12(6): 2365-2374.
|
| 8 |
Kojcev R, Fuerst B, Zettinig O, et al. Dual-robot ultrasound-guided needle placement: closing the planning-imaging-action loop [J]. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg, 2016, 11(6): 1173-1181.
|
| 9 |
Lin Y, Guo J, Yang X, et al. Online advance respiration prediction model for percutaneous puncture robotics [J]. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg, 2024, 19(3): 383-394.
|
| 10 |
Chen S, Wang F, Lin Y, et al. Ultrasound-guided needle insertion robotic system for percutaneous puncture [J]. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg, 2021, 16(3): 475-484.
|
| 11 |
Chen S, Li Z, Lin Y, et al. Automatic ultrasound scanning robotic system with optical waveguide-based force measurement [J]. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg, 2021, 16(6): 1015-1025.
|
| 12 |
田文, 孙辉, 贺青卿. 超声引导下甲状腺结节细针穿刺活检专家共识及操作指南(2018 版) [J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2018, 38(3): 6-9.
|
| 13 |
张颖, 张一峰, 徐辉雄. 2022 年甲状腺超声诊治研究进展 [J]. 肿瘤影像学, 2023, 32(5): 472-477.
|
| 14 |
Eszlinger M, Ullmann M, Ruschenburg I, et al. Low malignancy rates in fine-needle aspiration cytologies in a primary care setting in germany [J]. Thyroid, 2017, 27(11): 1385-1392.
|
| 15 |
Novoa E, Gürtler N, Arnoux A, et al. Role of ultrasound-guided coreneedle biopsy in the assessment of head and neck lesions: a metaanalysis and systematic review of the literature [J]. Head Neck, 2012,34(10): 1497-1503.
|
| 16 |
Chen S, Lin Y, Li Z, et al. Automatic and accurate needle detection in 2D ultrasound during robot-assisted needle insertion process [J]. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg, 2022, 17(2): 295-303.
|
| 17 |
Chen S, Wang F, Lin Y, et al. Ultrasound-guided needle insertion robotic system for percutaneous puncture [J]. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg, 2021, 16(3): 475-484.
|
| 18 |
姜纬, 邓学东, 杨忠, 等. 自由角度和改制后固定角度穿刺架引导下仿甲状腺细针抽吸穿刺体模实验 [J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2020,30(3): 489-492.
|
| 19 |
Liang P, Dong B, Yu X, et al. Prognostic factors for percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy of hepatic metastases [J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2003, 181(5): 1319-1325.
|
| 20 |
Fu Y, Sun Y, Pei Q, et al. Factors influencing the sample adequacy of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration from solid thyroid nodules for liquid-based cytology: a demographic, sonographic, and technical perspective [J]. Medicina (Kaunas), 2022, 58(11): 1639.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |